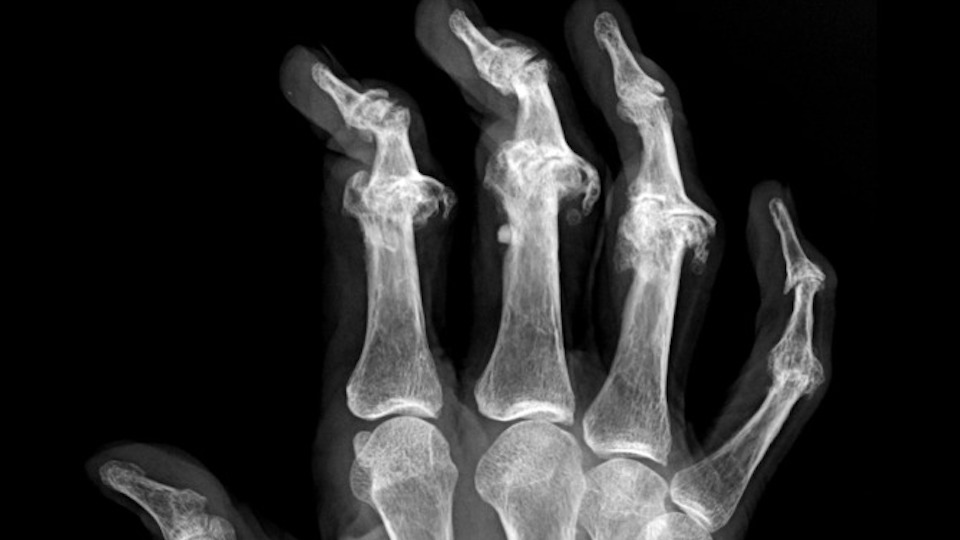
Psoriatic Arthritis
Up to 30 percent of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, an inflammatory form of arthritis.
Psoriatic arthritis can cause swelling, stiffness and pain in and around the joints, cause nail changes and overall fatigue.
Studies show that delaying treatment for psoriatic arthritis as little as six months can result in permanent joint damage. Early recognition, diagnosis and treatment of psoriatic arthritis are critical to relieve pain and inflammation and help prevent joint damage.
What are the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis can develop slowly with mild symptoms, or it can develop quickly and be severe. Early recognition, diagnosis and treatment of psoriatic arthritis can help prevent or limit extensive joint damage that occurs in later stages of the disease. The disease can develop in a joint after an injury and may seem like a cartilage tear.
Here are common symptoms of psoriatic arthritis:
- Generalised fatigue
- Tenderness, pain and swelling over tendons
- Swollen fingers and toes that look like sausages
- Stiffness, pain, throbbing, swelling and tenderness in one or more joints
- A reduced range of motion
- Morning stiffness and tiredness
- Nail changes—for example, the nail separates from the nail bed and/or becomes pitted and mimics fungus infections
- Redness and pain of the eye, such as conjunctivitis
Psoriatic arthritis usually affects the distal joints (those closest to the nail) in fingers or toes.
You may also experience symptoms in your lower back, wrists, knees or ankle.
In 85 percent of patients, psoriasis occurs before joint disease. If you have been diagnosed with psoriasis, it is important to tell your dermatologist if you have any aches and pains.
There is little connection between your psoriasis severity and psoriatic arthritis severity. Having a severe case of psoriasis does not necessarily mean a person will have a severe case of psoriatic arthritis. A person could have few skin lesions, but have many joints affected by the arthritis.
How is psoriatic arthritis diagnosed?
If you experience joint aches and pains, talk to a doctor about diagnosis and treatment. Working with primary-care doctors or dermatologists often is the first step in diagnosing psoriatic arthritis, but psoriatic arthritis patients should consider seeing a rheumatologist, a doctor who specialises in arthritis.
There is no definitive test for psoriatic arthritis. The diagnosis is made mostly by your doctor’s observations and by a process of elimination. Your doctor will need your medical history, particularly your history with psoriasis, and may perform a physical examination, blood tests, MRIs and X-rays of the joints that have symptoms to diagnose psoriatic arthritis.
The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis are similar to those of three other arthritic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, gout and reactive arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis generally involves joints symmetrically distributed on both sides of the body, and it may produce bumps under the skin that are not present in psoriatic arthritis. However, some forms of psoriatic arthritis look very similar. However, having psoriasis on the skin and nail changes are usually indicators of psoriatic arthritis.
To rule out rheumatoid arthritis, your doctor may test for a certain antibody, called a rheumatoid factor, that is normally present in rheumatoid arthritis. The rheumatoid factor is not usually found in the blood of psoriatic arthritis patients.
A person can have rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, but that is rare.
Likewise, it is possible to have gout along with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. If you have an excruciatingly painful attack in a joint, particularly in the big toe, you may want to have a test for gout. Your health care provider will want to examine fluid drawn from the affected joint for elevated serum uric acid levels, which would indicate gout.
However, people with psoriatic arthritis can have elevated serum uric acid levels, too, and not have gout. Taking a low-dose aspirin or increased skin cell turnover also can cause high serum uric acid levels.
It is important to distinguish between the two forms of arthritis, because they may be treated with different medications. Learn more about the differences between gout and psoriatic arthritis.
What kind of psoriatic arthritis do I have?
Just like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis ranges from mild to severe. Your rheumatologist will consider how many joints are affected before determining a treatment plan. Even a small number of inflamed joints, however, can have a profound impact on pain and function and factors into the treatment decisions.
Mild psoriatic arthritis is sometimes referred to as oligoarticular, meaning it affects four or fewer joints in the body.
Severe psoriatic arthritis is often referred to as polyarticular, meaning it affects four or more joints.
Spondylitis refers to inflammation of the spinal column. This occurs in some individuals with psoriatic arthritis. The main symptoms are inflammation with stiffness of the neck, lower back and sacroiliac joints. Spinal arthritis makes joint motion in these areas painful and difficult.
Enthesitis refers to inflammation of entheses, the site where ligaments or tendons insert into the bones. Common locations for enthesitis include the bottoms of the feet, the Achilles’ tendons, and the places where ligaments attach to the ribs, spine and pelvis. It is unique to psoriatic arthritis and does not occur with other forms of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Enthesitis can make the tissues in the affected area become ropey (known as fibrosis) or solid (known as ossification or calcification).
Dactylitis, or “sausage digits,” refers to inflammation/swelling of an entire finger or toe. It happens when the small joints and entheses of the surrounding tendons become inflamed. Dactylitis is another distinguishing indicator of psoriatic arthritis. Usually dactylitis involves a few fingers and/or toes, but not in a symmetrical pattern (different toes and fingers are affected on different sides of the body).
Psoriatic arthritis also can affect the joints of your arms and legs, including the elbows, wrists, hands and feet.
Treatments for psoriatic arthritis range from oral medications that reduce inflammation and swelling to biologic drugs that are injected or infused, and target specific parts of your immune system to combat psoriatic arthritis symptoms and slow joint damage.